You’ve surely seen news in the headlines about large companies that have experienced devastating cyberattacks. However, it’s not only large businesses that are affected. Small businesses are actually a bigger target for hackers because they don’t have the defenses that their larger counterparts do. That’s why it’s essential for cybersecurity to be a key component of your business management plan.
Although the definition of cybersecurity isn’t always agreed upon, it’s essentially the practice of ensuring the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of information. This includes the ability to defend against and recover from accidents like hard drive failures or power outages, and from attacks by adversaries.
Why does cybersecurity matter?
According to The U.S. 2017 State of Cybercrime Study:
- Cybercrime damage costs will hit $6 Trillion by 2021.
- Global spending on cybersecurity is predicted to exceed $1 Trillion by 2021.
- Ransomware damage costs will rise to $11.5 Billion in 2019.
- Businesses will fall victim to ransomware at a rate of every 14 seconds by the year 2019.
This is a very scary – not only in terms of money but in terms of the survival of your business. If your clients find out that you were breached, they’ll simply take their business to your competitors.
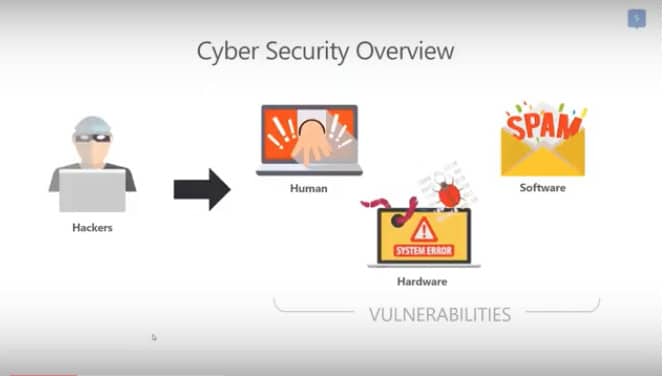
Hackers work 24/7 to find weaknesses and vulnerabilities in businesses like yours. There are three ways they do this:
1. Physical Hardware Hacking: This is where a criminal gets into your computer or laptop and installs malicious software (malware) to corrupt, delete or steal your data.
2. Software Hacking: Where cybercriminals find holes in your software to trick it into doing things it shouldn’t (like revealing your information).
3. Via the Human Component: Where they disguise emails as legitimate to fool you into providing confidential information like passwords and other credentials, so they can access your accounts and steal your money.
These Are the Most Common Cybersecurity Threats to Watch Out For:
- Social Engineering Attacks
- Ransomware
- Digital impersonations of executives and managers
- Data loss and compromised data
- Viruses
- Physical Incidents
Education, Awareness, and Preparedness Is Key.
To protect your organization, you and your employees must be aware of these threats and how to mitigate them. You should also make sure your software is up to date and patched as required, and that your hardware is protected and only accessible to authorized users. Plus, you should have access to IT professionals who can help keep your data safe and step in if a breach does occur.

Social Engineering Attacks
Social Engineering Attacks are where hackers exploit the one weakness that is found in each and every organization–human psychology. It’s essential that you educate your staff on these threats as they’re your first line of defense.
Hackers will try to exploit your employees with:
- Phishing – they lure email recipients and Web users into believing that a fraudulent website is legitimate. The phishing victim later discovers his or her personal identity and vital information have been stolen.

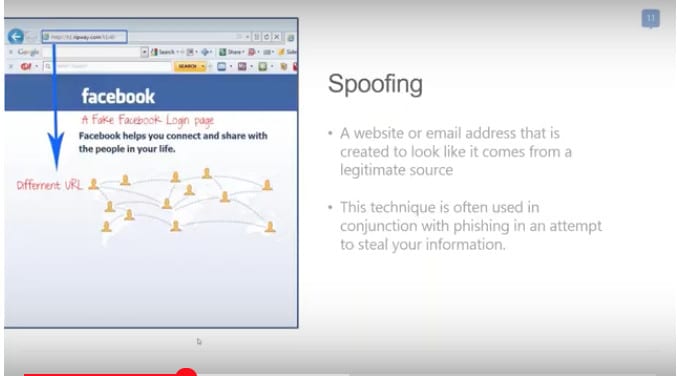
- Spoofing – the hacker creates a fake website with an expected URL, then prompts the user for personal information.
Follow these tips:
Stay informed about phishing and spoofing techniques. Regular security awareness training should be a top priority for your organization.
Stop and think before you click a link. Don’t click on links from random emails or text messages. Hover your mouse arrow over a link to see who sent it. Most phishing emails begin with “Dear Customer”, so watch out for these. Verify the website’s phone number before placing any calls. Remember, a secure website always starts with “https”.
Never divulge personal information requested by email. Phishing attempts try to send you to a webpage to enter your financial or personal information. If you suspect this, give the company a call. Never send sensitive information in an email to anyone.
Be skeptical of messages that contain an urgent call to action:
- With an immediate need to address a problem that requires you to verify information.
- That urgently asks for your help.
- Asking you to donate to a charitable cause.
- Indicating you are a “Winner” in a lottery or other contest, or that you’ve inherited money from a deceased relative.
Consider installing an anti-phishing toolbar and security tools. Some Internet browsers offer free, anti-phishing toolbars that can run quick checks on the sites you visit. If a malicious site shows up, the toolbar will alert you.

Never download files from suspicious emails or websites. Double check the website URL for legitimacy by typing the actual address into your Web browser. Check the site’s security certificate. Also, beware of pop-ups as they may be phishing attempts.
Block pop-ups via your browser settings. You can allow them on a case-by-case basis if you decide to.
Change your passwords often. Consider using a password manager like Dashlane or LastPass that will automatically insert new, hard-to-crack passwords for you.
Don’t ignore messages to update your browsers and download the updates as soon as they’re available.
Ransomware
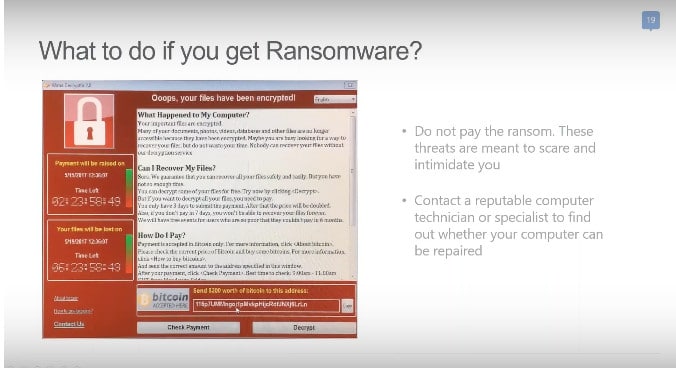
Ransomware blocks access to your data until you make a payment through an anonymous system like Bitcoin. Criminals are making millions of dollars by extorting money in exchange for a promise to unlock computer files.
If you believe a ransomware attack is occurring and your files are being encrypted, power off your machine right away. Unplug the power cord if you can’t do this with the power button.
Whatever you do, don’t pay the ransom! A lot of people believe that if they pay the ransom, their data will be released, but this isn’t always the case. 1 in 4 victims who pay a ransom never recover their data. Even the FBI urges people not to pay.
Important! Backup your data to a reliable offsite location and a physical hard drive backup that can be removed from your device. If your data is held for ransom, you’ll always have your backup.
Viruses
A computer virus is a computer program that can duplicate itself and easily spread from one computer to another, destroying important files and often damaging your computer. In most instances, you’ve actually installed the virus yourself because they often hide within browser plug-ins, programs, and downloads.
Viruses can breach your defenses and lock down your computer files using strong encryption. They can do a lot of damage and spread to others’ computers via email and the cloud. They can:
- Send spam.
- Provide criminals with access to your computer.
- Scan and find confidential information.
- Hijack your web browser.
- Disable your security settings.
Make sure you use a professional, up-to-date antivirus on your computers to detect and eradicate the latest viruses. Investing a bit more and making sure you have a decent antivirus is critical because there are a lot of viruses out there today.

Malware goes into your software, browser, or operating system and alters it to steal information.
Trojan horses were big in the early 2000’s and disappeared for a while, but they’re back. It looks like a legitimate piece of software, but in the back end, it can do anything malware can do.
Spyware is similar to malware but exists in the background and watches what you do. It sends this information to the criminal. Most of this comes in free downloads of software.

People often forget about keeping their IT equipment safeguarded and locked down. Cybercriminals also steal your information physically. They may try to take your laptop computer or insert a USB drive into your computer to steal your data. They may also try to physically watch you and your employees when you’re working on laptops in coffee shops, airports, and in other public venues. Also, make sure to have your computer screen go dark or computer shut off automatically when you’re not using it.
Be sure to use the latest operating systems and install updates as soon as they’re released. Microsoft and other software companies don’t support these outdated systems, so you’re left vulnerable without any protections. If one computer is infected, your entire network can be as well.

Be sure to keep up to date on the latest cyber threats and what’s going on in the cybersecurity world.
Contact us!

The Cybersecurity Experts at K2 Technologies will be happy to train your employees to recognize cyber threats, and we can protect your IT assets while we’re at it. Call (888) 686-3025 or send an email to [email protected]. We’re always here to help.

 Mon-Fri 9 AM to 5 PM Mountain
Mon-Fri 9 AM to 5 PM Mountain 888-686-3025
888-686-3025



